EPS geofoam can be easily cut and shaped on a project site, which further reduces jobsite challenges. EPS geofoam is available in numerous material types that can be chosen by the designer for a specific application. Its service life is comparable to other construction materials and it will retain its physical properties under engineered conditions of use.
There are numerous manufacturers and suppliers of EPS geofoam in North America. Expanded polystyrene is created in a two-stage, molded bead process. EPS geofoam is produced in blocks that can be cut into various shapes and sizes – and a range of compressive resistances – to suit specific project needs. As an engineered product, it can be produced to obtain the required compressive resistance. EPS geofoam density, only about 1% that of soil and rock, is controlled during the manufacturing process, making it a superior, ultra-lightweight fill material that significantly reduces the stress on underlying subgrades. The lighter load can reduce settlements and can improve stability against bearing and slope failures.
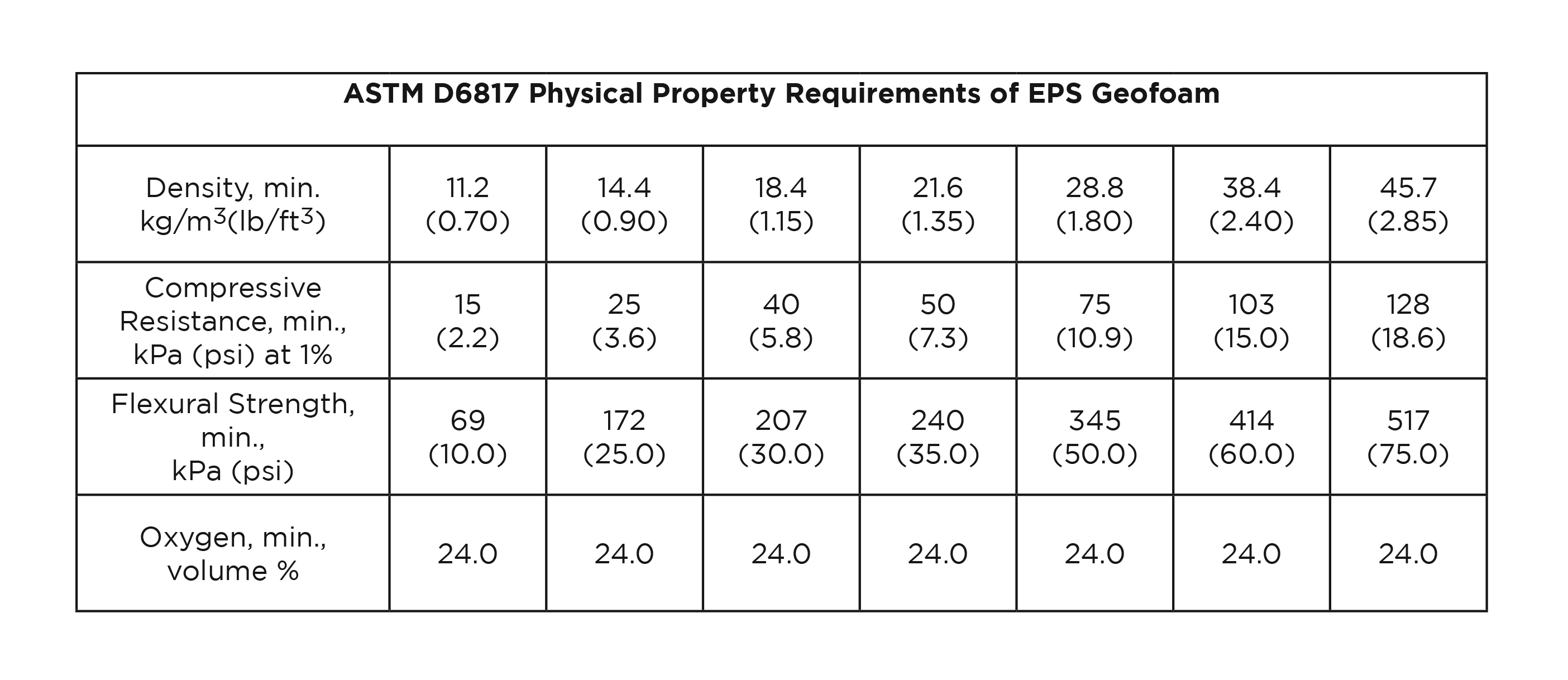
GEOFOAM PROPERTIES
GEOFOAM APPLICATIONS
EPS geofoam is inherently multi-functional, which makes it effective to use in a wide variety of applications. It offers special advantages for construction on soft ground, slope stabilization and retaining walls. EPS geofoam has been used in road and airfield pavements and railway track systems, beneath refrigerated storage buildings, sports arenas and storage tanks to prevent ground freezing and heaving and in below-ground building segments to reduce seasonal heating and cooling requirements.
EPS geofoam enables engineers, architects, and builders to design for key geosynthetic functions and select the best combination of products to achieve project goals. With unprecedented strength and flexibility, EPS geofoam also offers innovative solutions to a range of problems, including protection from earthquake shock and noise and vibration dampening.